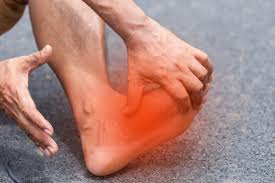
Issues related to the transverse arch of the foot can contribute to various foot problems and discomfort. They may cause due to the collapsing, compressing and over stress.
Metatarsalgia:Description: Metatarsalgia is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, particularly around the metatarsal heads (the heads of the long bones in the foot).
Connection to Transverse Arch: If the transverse arch is not properly supported or if there is excessive pressure on the metatarsal heads, it can lead to metatarsalgia.
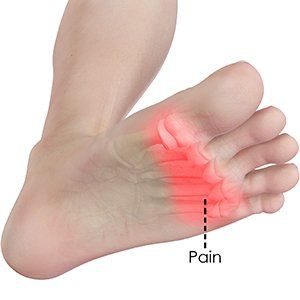
Morton's Neuroma:
Description: Morton's neuroma is a painful condition that involves a thickening of the tissue around the nerves leading to the toes, often causing pain and discomfort between the third and fourth toes.
Connection to Transverse Arch: Issues with the transverse arch can contribute to nerve compression, leading to the development of Morton's neuroma.
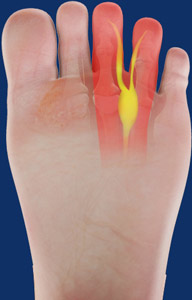
Foot Fatigue and Pain:
Description: Insufficient support for the transverse arch can result in overall foot fatigue and pain, especially during prolonged periods of standing or walking.
Connection to Transverse Arch: The transverse arch plays a role in weight distribution and shock absorption. If it is not adequately supported, the foot may experience increased stress and discomfort.
Flat Feet (Pes Planus):
Description: Flat feet occur when the arches of the foot, including the transverse arch, collapse, causing the entire sole to come into contact with the ground.
Connection to Transverse Arch: Weakness or lack of support in the transverse arch can contribute to the development of flat feet.

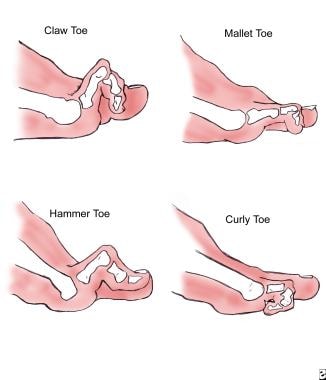
Toe Deformities:
Description: Transverse arch issues can contribute to the development of toe deformities, such as hammertoes or claw toes, where the toes are bent abnormally.
Connection to Transverse Arch: Altered biomechanics due to transverse arch problems can lead to imbalances and deformities in the toes. Moreover, the compression of the shoes also plays a major role.
Author
Dr. Durga Saravanan (PT)., MSc Sports biomechanics and kinesiology.